Recent post

Do you want to whiten your teeth? Contact your stomatologist first and make sure that the treatment will be safe for you. Teeth are a very important part of a person's appearance. On the grounds of somebody's teeth condition we can tell a lot about this person. This is why the treatments such as teeth whitening and plaque removal are becoming more and more popular. ... .
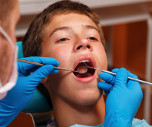
A treatment has to be conducted whenever a malocclusion is diagnosed. Otherwise, it may cause face deformation or have many undesirable health consequences. ... .

Who wouldn't like to have white teeth? In reality, just a few people have an ideally white smile, though, everybody dreams about it. On the market we can now get chewing gums which - according to the producers - possess whitening qualities. Do tooth whitening chewing gums work at whitening teeth? ... .
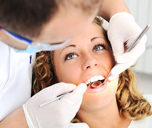
Are you a little confused about which whitening method to choose? To count on a cheaper home remedy or to trust a specialist? Find out what produce the best effects! ... .
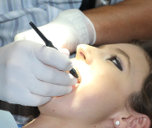
Beautiful, white and ideally aligned teeth are the beauty ideal. In order to enjoy it, it is not enough to just pay attention to the oral hygiene. It is necessary to prevent and treat malocclusions. ... .